The history of climate changes is not a short one. The notion that human activity could affect the planet's weather patterns was thought to be absurd for centuries. The ancient Greeks suggested that humans could alter the weather by plowing fields or cutting down trees. Scientists finally accepted that humans could change the climate in the 20th-century.
Scientists began collecting data in the 1950s on the impacts of greenhouse gases on climate. The "Keeling Curve", an graph showing the rise in CO2 levels over the years, was one the first scientific discoveries. This was one among the most important scientific discoveries in the 20th Century and was evidence of the greenhouse effects.

After World War II ended, governments started to talk about how to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Increased global temperatures would cause more droughts and stronger hurricanes, scientists predicted. Some scientists even warned that there could be an ice age. But scientists stopped issuing warnings after the cooling phase ended.
The temperature had started to rise by mid-1980s. The United States was hit with droughts and wildfires in 1988, as it reached its highest point. A series of climatic incidents confirmed that global warming theory is true.
In the 1970s, scientists noticed that aerosol particles could block sunlight. In addition to air pollution, the Second Industrial Revolution introduced electricity and fertilizers into the atmosphere. They also increased greenhouse gas emissions by speeding up the clearing of land.
Another key milestone in the history of climate change is the creation of the Montreal Protocol in 1987. This protocol mandated the total ban of chlorofluorocarbons. Based on research conducted by three scientists, it was based upon abnormally low levels of ozone over the South Pole in 1985.

1972 was the year of the United Nations Scientific Conference, which convened the very first Earth Summit. It took place in Stockholm, Sweden. The conference issued a declaration addressing the human environment. It also called for monitoring climate change. It also established the Governing Board, United Nations Environment Programme, and the Environment Coordination Board. These bodies developed acid rain programs and a program for the protection of the ozone layer.
Journalists, businessmen, and politicians all had an interest in global warming. Popular magazines described it as a possible indicator of an impending global ice age. Also, there were predictions of severe heat waves or droughts. Although these warnings were not substantiated, they gained significant attention.
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) was the first international treaty that addressed global warming. It was designed to decrease the emissions of greenhouse gases from industrialised countries. The Kyoto Protocol, which was signed in 1997, became effective on January 1, 2005.
The Paris Agreement took over the Kyoto Protocol in 2015. It set a goal of keeping global warming below 1.5 degrees Celsius. These countries must reduce their carbon emissions. If this isn't done, the Earth might suffer devastating consequences.
FAQ
How can the impact of climate change be reduced or mitigated?
There are various measures that can be taken to reduce and mitigate the effects of climate change. There are many ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These include using more sustainable energy and alternative sources of power. Protecting forests and wilderness habitats. Investing in sustainable transport systems. Strengthening early warning systems for natural disasters. Creating a research program about the impacts of climate change on biodiversity. Investing in green technologies like solar panels and wind turbines. Developing sustainable consumption habits and implementing appropriate environmental regulations in all areas of society. It is important to raise awareness of climate change in order to encourage people and make them feel responsible for their actions.
What are the effects of climate change on the environment and society?
Climate change has many impacts on society and the environment. Rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and decreased air quality are just some of the environmental impacts of climate change. These changes could have serious consequences for humans, causing instability in communities, intensifying poverty, insect-borne illnesses, changing human migration patterns, and destroying essential habitats.
Already, climate disruption is already having profound impacts on the environment and society around the world. As global temperatures continue to rise, this is likely to worsen in the near future.
The most significant effect of climate change globally is the rise in ocean levels caused by melting ice caps. This causes shoreline erosion along many coastlines and increases the risk of flooding for coastal communities. Also, saltwater intrusion occurs, which negatively affects freshwater supplies in coastal areas in many countries.
Due to climate change, extreme weather phenomena such as heatwaves/droughts frequently occur across many countries in the world. These events cause mass destruction to homes and businesses, leading to displacement or relocation of communities or wiping out whole towns in some cases. Extreme storms also present risks of flooding or landslides which can cause further damage to infrastructure, such as roads and railways.
Additionally, wildfires caused climate change are more common than ever. They can be devastating for both the habitats and the people who live nearby.
These drastic changes often lead to displacement or refugee crises. People move out of their homes involuntarily or voluntarily when their communities become unsafe or uninhabitable due to the altered climate.
An increase in aridity means that dust storms can occur more frequently, making people with asthma and other respiratory illnesses like asthma particularly vulnerable. In addition, pest infestations are expected to increase significantly linked with higher temperature extremes - a phenomenon known as 'greenhouse bug' - leading to further damage to agricultural production that further affects global food insecurity numbers as fewer crops become available at worse nutritional qualities potentially bringing additional hardships upon marginalized populations already barely able make ends meet otherwise.
What are the causes for climate change
Climate change is a worldwide phenomenon caused by an increase of human-generated greenhouse gasses emitted into the atmosphere. This is mainly due to fossil fuel burning for power and transportation. These greenhouse gases trap more heat from the sun, which causes global warming.
Climate change can also be caused by population growth, land clearing, destruction of ecosystems and energy consumption, over-grazing, and deforestation. This further decreases the number natural carbon sinks that absorb CO2 in the atmosphere. Climate change may also be caused by natural factors such as changes to solar radiation.
These combined human activities result in overloading Earth's capacity to properly balance its energy budget, leading to an average increase of 1 degree Celsius globally since pre-industrial times. Glaciers melt faster than they form and sea levels rise as oceans absorb most of this heat energy. Other adverse consequences include water shortages and droughts as well as extreme weather events, such as flooding and hurricanes, which are often caused by heavy rains on soils.
To protect ourselves from further damage, it is essential for us to reduce our carbon footprint and start curbing our emissions now so that we have a fighting chance against the already significant impacts of climate change. Reducing our dependence on fossil fuels for electricity production is crucial alongside investing in renewable sources - think wind turbines or solar panels - which do not emit any harmful pollutants into the environment. Other sustainable practices like reforestation can also help restore some balance around these delicate planetary cycles we rely on for survival.
What is the effect of climate change upon biodiversity and ecosystems?
Climate change can have a variety of impacts on biodiversity, ecosystems, and the environment. Rising temperatures, changing extreme weather events and sea level, as well as an increase in acidity in oceans, are all issues that affect wildlife and ecosystems.
These climate changes can alter habitat areas and food chains, as well as affect species distributions or population numbers. They could also have significant consequences for biodiversity or the functioning of ecosystems. Water availability can be affected by changes in hydrological cycles.
Moreover, changes to climate result in rising temperatures and more frequent extremes such as droughts and floods which puts more stress on already fragile systems such as coral reefs or tropical rainforests. It is estimated that up to 30% of animal species could become extinct due to climate change by 2050, which would spark a cascade of further losses within ecological communities.
Climate change poses a significant threat to biodiversity and human societies, as well as to ecosystems that provide food, water, timber, or other services. It is essential to mitigate its effects at all levels. Future damages must be avoided by careful management.
How does human activity contribute to climate change?
Climate change is a major contributor to human activity. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC) states that humans are responsible more than 70% for global warming in the past 20 years.
Burning Fossil Fuels: Burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This raises the already existing atmospheric levels of CO2 which acts as an "greenhouse gas", trapping heat from Earth's surface and increasing temperatures. This can result in an increase in ocean levels due to Arctic ice melting. This creates unpredictable weather patterns that can disrupt food production and threaten human health.
Deforestation: Deforestation knocks out trees which sequester atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks when they take it up during photosynthesis. Reduced forest cover can also increase albedo, which is the amount of reflected sunlight coming back into space. This reduces solar heat absorption at the surface of the earth and promotes global warming. It also reduces the quality of local air, with deforestation being permanently linked to respiratory problems.
Farming: The animal agriculture industry contributes 14%-18% of total anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases globally every year. Large amounts of methane gas are released by animal waste due to its richness in methane bacteria. Eating less or none of these products can reduce global warming.
In conclusion, human activity has been drastically impacting our environment for centuries now, but with rapid advances made in technology such as renewable energy sources availability we have started turning our heads towards the future leaving behind carbon-emitting heavy industries results will soon start speaking themselves clearly when we leverage on technology through green innovation paving away toward eco-friendly efforts combatting climate change efficiently keeping everyone safe under prosperous nature purview.
What role does the energy sector play in climate change? How can this be addressed?
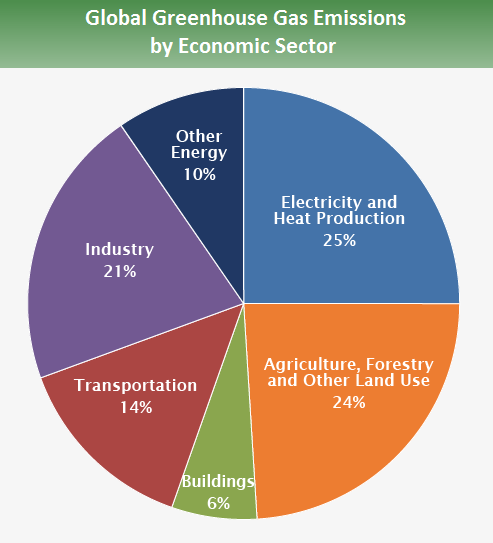
It is crucial that the energy sector plays a significant role in climate change. The main source of global warming comes from the burning of fossil energy. It releases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, traps heat, and results in an increase on Earth's average temperature.
To address this issue, energy sources must transition away from carbon-emitting fuels like coal and natural gaz and instead turn to renewable energy sources like solar, geothermal, wind, and other renewable sources. This shift can be made possible by both government policy and incentives as well investments in innovative technology like hydrogen-fuel cells. By investing in infrastructure that supports the use of these renewable sources, businesses and households can drive down emissions while simultaneously reducing their electricity bills.
Alternatives include moving away from polluting vehicles like petrol-powered cars and moving to electric vehicles or public transportation. The government has great power to help societies transition away from oil-based infrastructures. They can support research into battery technology and encourage consumers to invest in cleaner modes.
In order to reduce their carbon footprint, companies need to adopt green business methods. These include installing better insulation systems in offices and creating energy efficiency plans for manufacturing facilities. This can dramatically reduce operational costs, while improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives must not only be supported at the company level, but also at the federal level to be truly successful. Taxing pollution products increases individuals' willingness to adopt healthier practices. But this won't force them to compete with polluters. Instead, vouchers or subsidies for low carbon products will create a continuous market to support sustainability. This is why tackling climate changes requires both private industry as well as private citizens to make a difference. By switching to green energy and adopting environmentally friendly practices, we can help to ensure that the future generations of people are affected positively.
What does climate change politics have to do with global efforts to combat it?
Climate change has become a highly politicized topic that has caused great divisions among governments, nations, and individuals. The implementation of measures to address climate change is affected by the political stances of various actors. It has become difficult to find consensus on global efforts to tackle this pressing environmental crisis.
The vast majority of scientific opinion agrees that human-generated climate change is real and requires urgent action. The politics surrounding these issues often undermines global cooperation which is needed to make effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices, upholding regulations protecting natural habitats, researching viable technological solutions, and other climate change interventions.
Many governments across the globe are determined to protect their own economic interests and enforce regulations that restrict business activities. This frequently clashes with the regulations that experts recommend in order to tackle climate change effectively. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
The difficulty of reaching a full consensus about the best way to combat climate change is further complicated by differences in power dynamics. Countries with more economic power frequently appoint their own representatives for international negotiations over the environment. This can lead lopsided discussions between countries' perceived interests and those of all other parties. A number of potential side effects that could be caused by radical changes like geoengineering were also discussed at national and international levels.
In the same way, grassroots movements are fighting powerful opponents at the grassroots level. These include corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbyists looking to retain politically favorable positions.
It is essential to distribute resources properly to any intervention program, and to be mindful of political divisions within nations, if we want to see an effective coordinated effort to mitigate our current environmental crisis.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest In Clean Energy and Support the Transition To A Low-Carbon Future
Clean energy is a form of renewable energy that does not produce pollution or emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. It includes technologies such as solar photovoltaic, wind power, hydroelectricity, geothermal energy, and hydrogen fuel cells. Renewable energy sources have many environmental benefits. This includes a decreased reliance on fossil oil, a decrease in air pollution caused by traditional electricity methods, as well as providing reliable electric access to remote locations.
Investors have the opportunity to invest in clean-energy projects by purchasing shares of companies that create innovative technologies. This can include investing in publically traded stocks, mutual funds, and ETFs (exchange-traded funds) related to renewable energy. Investors may also be interested in direct investments in start ups or venture capital projects that fund research and technology development.
Investors who invest in clean energy are supporting innovation that helps reduce harmful emissions from traditional sources of electricity generation. This investment could also result in increased economic development, as it creates jobs for skilled labor and engineers related to the production renewable energy systems. Finally, putting money into clean energy can provide investors with a financial return due to tax incentives programs that are incentivizing investments into green technologies like wind farms, solar panels, and biomass heat generation systems.
We can help the transition to low-carbon by investing in companies that create electricity from renewable resources.