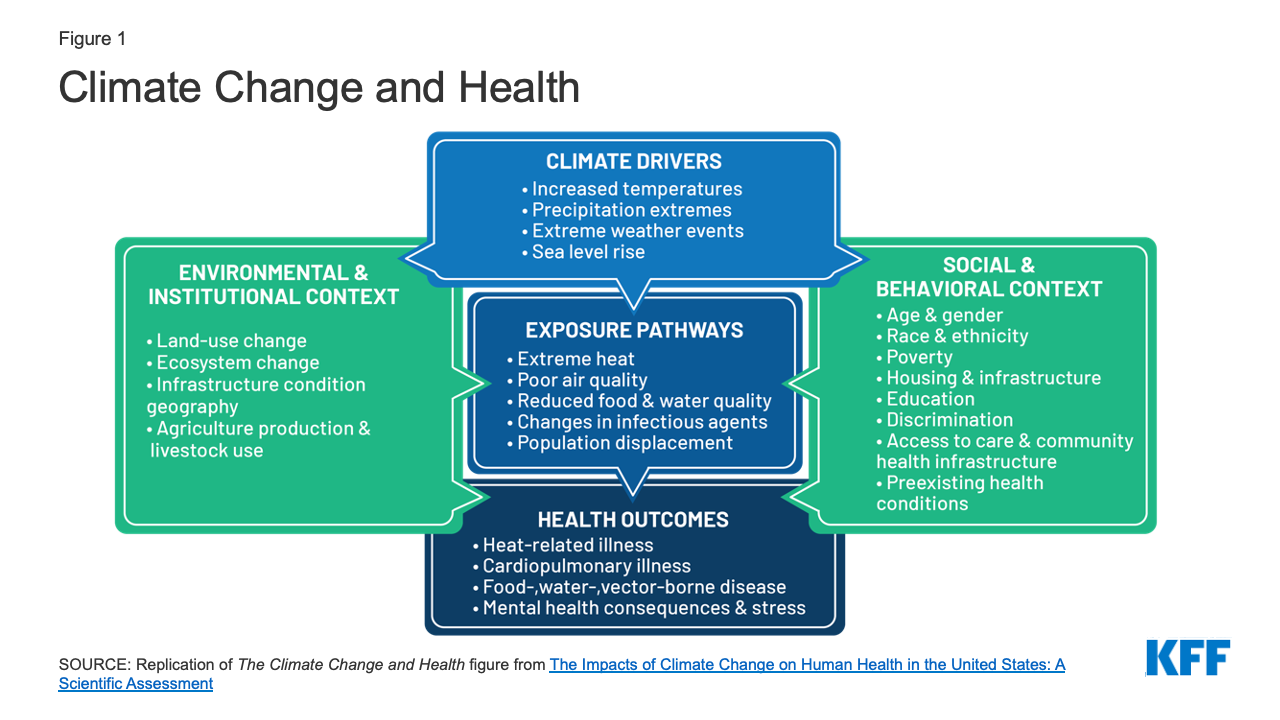
Climate change mitigation refers to the measures taken to stop the climate changing. These actions include reducing greenhouse gases emissions, removing pollution from the atmosphere and improving energy efficiency. In April 2019, the first workshop was held to identify mitigation options to address climate change.
In October, another workshop was held. It aimed at assessing the well being effects of demand-side reduction options. This was accomplished by a comprehensive literature review. This review looked at a number of methods to evaluate the link between climate change mitigation & well-being. It included the work of a group of experts, including well-being and technology experts, academics, and other professionals. Additionally, the cobenefit model was used to assess well-being.
Demand-side solutions aim to change the choices of consumers or businesses by increasing the demand for goods, and services. They are distinct from supply-side solutions, which focus on changing production technologies, production processes, or consumption patterns. Increasing the adoption of sustainable practices and promoting sustainable land and forests are examples of demand-side strategies.
Demand-side strategies can be grouped into several categories. The "shift" category refers specifically to a strategy for switching to low-carbon technology. Some of these strategies include increasing availability of electric cars, developing more sustainable transportation, and reforestation. Other strategies are focused upon reducing unnecessary consumption. It is important to model more behavioral consequences of such actions.
While the majority of research has been done from a macroeconomic viewpoint, many social dimensions have been overlooked. There should be more research to discover how people's values, beliefs and worldviews influence their decisions as well the impact of climate mitigation measures on their wellbeing. Research on the relation between the various mitigation options and the relevant social components, such as economic and social well-being, is required.
There are three main limitations to the joint evaluation of climate change mitigation and well-being. First, the eudaimonic perspective, which emphasizes concrete conditions for a better life, isn't as prominent in the context of climate mitigation. Second, current GHG emission assessment is limited to a macroeconomic viewpoint. Third, more specialized research is needed to better understand how the broader climate change mitigation options and the social constituents involved can impact well-being.

A team of nine experts conducted the first workshop. It involved a brainstorming session that identified potential demand-side solutions to climate change. The participants were separated into three groups: health and well being, infrastructure and industry. The upper boundaries of each area were determined in rounded numbers during the internal review.
The workshops, which addressed the wellbeing aspects of demand side mitigation options, discussed the consequences of these policies for citizens' well-being. They also considered the possibility of evaluating well being using the eudaimonic model.
FAQ
What is the role of greenhouse gases in climate change?
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act like an invisible blanket surrounding the Earth, trapping the infrared radiation that warms it and keeping it from getting too hot. Without them, our planet would be much cooler than it is now.
The human activity of burning fossil fuels, or other industries that generate emissions, can create greenhouse gases. These activities will continue to increase heat trapping in the atmosphere. This will lead to increasing temperatures and extreme weather conditions.
The most prevalent greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide, which is released from fossil fuels, such as oil, gas, and coal. Climate change is also caused by major greenhouse gases like methane (CH4) and nitrous oxides (N2O).
Because of human activities, the concentrations of greenhouse gases have increased substantially since preindustrial days. This has led worldwide warming and increased temperatures in the oceans as well as all over the planet. It is also leading to changes such as intense storms and droughts; melting glaciers; and rising seas.
To prevent further climate change-related damage, humanity must reduce its greenhouse gas emissions by moving away from fossil fuels and towards renewable energy sources like wind or solar power. There are also ways to reduce CO2 emissions, such as by planting trees and using agricultural techniques that absorb more of the gas. These activities will lower the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gasses and make the Earth a more healthy place for all life.
How is extreme weather related to climate change
Global warming directly links extreme weather events like heat waves, floods. droughts. cyclones. storms. Global warming has caused an increase of atmospheric temperatures.
According to climate scientists the average frequency for extreme weather-related events has increased more than twofold since 1980. Rising ocean water temperature causes sea levels to go up as well as changing wind patterns. This affects the normal distribution of storms and hurricanes in different geographical regions across the planet.
2015 El Nino brought warm water towards South America. This led to increasing temperatures at an alarming pace and heavy rains that caused floods and displacement in Peru, Bolivia and other countries. Many places, including Antarctica had their highest-ever temperatures. This suggests a connection between global warming trends or the occurrence or frequency in extreme weather events.
Another example is Hurricane Irma, which struck in 2017, causing $50 billion in economic damage not only to Florida, but also to other states like Puerto Rico, Cuba, and others. This proves once again that climate change has been responsible for an increase in major storms.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, (IPCC), concluded that human activities are increasing severity of climate change. This naturally leads, in turn, to more severe and intense natural disasters globally. Thus, there is strong evidence concerning humans' relationship to extreme weather events occurring around us all.
What is the current global climate? And how is it changing over time?
The current climate situation is one of uncertainty and unprecedented change. Temperatures are increasing dramatically due to increased atmospheric carbon dioxide, which is leading to heat waves, droughts and changes in rainfall patterns.
These changes already have a profound effect on ecosystems all over the globe, causing habitat destruction and extinctions. They also threaten the livelihoods and lives of billions, especially in areas that are already suffering from resource scarcity and poverty.
Human activity has led to an increase in extreme weather events such as hurricanes, cyclones, floods, wildfires, etc. As temperatures continue their climb, this trend is expected to continue.
Global climate change is causing many problems. These include rising food insecurity, displacement due to extreme weather events and sea level rise that force communities to move. Climate change is also increasing social inequality bydisproportionately impacting marginalized communities who lack the necessary resources and knowledge to adapt.
While progress has been made in some countries in terms of reducing carbon emission or developing renewable energy programs, there has yet to be any meaningful action taken at a global scale that would allow us to address these issues effectively. All nations must unite to prevent further destruction and devastation by climate change.
What impact does climate change have on biodiversity and ecosystems
Climate change can have many impacts on biodiversity and ecosystems. The most pressing issues facing wildlife and ecosystems are rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and increased acidity.
These changes can result in shifts of habitat areas, disrupting food chains or affecting population numbers or distributions. With potentially devastating consequences for biodiversity, ecosystems and their functioning, these shifts in climate conditions could cause significant impacts. Changes in the hydrological cycles can also have an impact on water availability for species that live in aquatic environments.
Climate changes can lead to higher temperatures and more frequent extremes (such as droughts) which put more stress on already fragile systems, like coral reefs or tropical forests. Up to 30% of all animal species could be extinct by 2050 due to climate change, which would lead to further losses in ecological communities.
Climate change is a serious threat to biodiversity as well as human societies that rely on functioning ecosystems for food and fresh water. The best way to minimize its impact is to work at every level to reduce global warming trends. Future damages can be avoided with prudent management practices.
What are the causes and consequences of climate change?
Climate change is a global phenomenon. It has been caused by an increase in greenhouse gases that are emitted from humans. These greenhouse gases trap more heat from the sun, which causes global warming.
Climate change can also be caused by population growth, land clearing, destruction of ecosystems and energy consumption, over-grazing, and deforestation. This also reduces the number naturally occurring carbon sinks, which absorb CO2 from atmosphere. Natural forces such as changes in solar radiation can also contribute to climate change.
These human activities together result in Earth experiencing an overloading of its energy budget. This has caused an average global rise of 1° Celsius over pre-industrial time. Because oceans absorb the majority of heat energy, glaciers are more likely to melt than they ever form. Other consequences include water shortages, droughts, and extreme weather events such as floods and hurricanes that are caused by heavy rainfall on saturated soils.
It is vital that we reduce our carbon footprint immediately and stop releasing greenhouse gases. This will help us protect ourselves against further damage from climate change. Along with reducing our dependence upon fossil fuels to generate electricity, it is important to invest in renewable sources like wind turbines or solar cells that do not emit harmful pollutants into nature. Reforestation and other sustainable practices can help restore balance to these delicate planetary cycles that we depend on for our survival.
Statistics
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest in Clean Energy, and Support the Transition to Low-Carbon Future
Clean energy is a form of renewable energy that does not produce pollution or emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. It encompasses technologies like solar photovoltaics and wind power. Investing in clean energy sources can have many environmental benefits, such as reducing reliance on fossil fuels, reducing the amount of air pollution generated by traditional electricity methods, and providing more reliable electrical access to remote locations.
By buying shares in companies involved in developing clean energy technologies, investors can get involved in these projects. This includes investing directly in stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) related to clean energy. Investors may also be interested in direct investments in start ups or venture capital projects that fund research and technology development.
Clean energy investors are supporting innovation that helps to reduce harmful emissions from conventional sources of electricity generation. This investment could also result in increased economic development, as it creates jobs for skilled labor and engineers related to the production renewable energy systems. Lastly, investors may see a return on their investment in clean energy through tax incentives programs. These incentives encourage green technology investments such as solar panels, wind farms, and biomass heat production systems.
By investing in companies focused on creating cleaner sources of electricity from renewable resources such as sun, wind, and water while avoiding activities that could harm the environment, we can support the transition to a low-carbon future while reaping economic rewards at the same time.