Earth is the only planet of the solar system with life. But how did life start on Earth? Scientists believe the earliest forms and stages of life were formed before the planet developed fully. Scientists also believe that there may be more species of life on Earth than is currently known.
Life on Earth is dependent upon a supply of liquid water. This is done through the water cycle. It involves three phases. The oceans hold the most water on the planet. However, there are large rivers and lakes. In addition, underground aquifers contain liquid water.

As the Earth heats, chemicals rise up to the surface, creating the atmosphere. Radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay to produce heat. Some of this heat remains in the Earth's inner core. Organisms also release radioactive elements into the atmosphere. This is why scientists think that the temperature in the outer core is about 6,700 to 7,800 degrees F. However it is possible that the inner one may be even higher.
Methanogens were responsible for high levels methane production in the early stages of life. These methane molecules were able to block ultraviolet light waves from reaching Earth's surface. They also allowed for the creation of the ozone layer. A few more years later, organisms began forming on the Earth's surface.
These changes caused the Earth's surface to change. Rain began to fall eventually. There were also some changes in the seasons. This was due in part to uneven heating of the sun.
The sun would eventually become a red-giant. The Earth would become more spherical due to its gravitational force. When this occurred, the equator pointing toward the sun and the North and South hemispheres pointing away from the sun.

A huge impact on Earth caused another change to the planet. This caused some of the ingredients to be ejected from the moon. Most of the heavier things fell to the middle of the planet. Lighter stuff rose up to the top. The earth was liquid at the time.
Earth is today a round planet, shaped like an apple. Its circumference, at the equator, is more than its diameter of 12,700 kilometers (7.900 mi). Depending upon your speed, you may reach the center of Earth in five to seven kilometers.
Within the planet, the lithosphere and the mantle make up 84% of its volume. The lithosphere consists of heavy rocks while the mantle consists of molten rock. The Earth's surface is 80-550 kilometers high, and the lithosphere lies at that elevation.
The mantle is composed of rock that has been melted during volcanic eruptions. As the Earth heats up, so does the pressure in its mantle. The molten rock is forced to the surface. During volcanic eruptions, lava is thrown out of the volcano, which generates heat that will rise to the surface.
FAQ
How can climate change be mitigated or reduced in its impact?
There are various measures that can be taken to reduce and mitigate the effects of climate change. These include reducing greenhouse gases emissions by using better energy practices and other sources of electricity, improving land management, protecting forests and wild places, protecting against extreme weather, investing in sustainable transport, strengthening early warning system for disasters, starting a research programme on the impact climate change has on biodiversity and ecosystems. Also investing in green technologies like solar cells or wind turbines, encouraging sustainable consume habits, and implementing environmental regulations across all segments of society. It's also important to educate the public about climate change. This will encourage people to be responsible for their actions.
How does the politics of climate change impact global efforts to address it?
Climate change is a controversial issue that has caused a lot of division between nations, governments and individuals. Politicians of many actors influence the implementation of actions to address climate change. It has been difficult for global consensus to address this urgent environment crisis.
The overwhelming majority of scientists agree with the fact that human-generated global warming is real. It is urgent for action to address it. The politics surrounding these issues often undermines global cooperation which is needed to make effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices, upholding regulations protecting natural habitats, researching viable technological solutions, and other climate change interventions.
Many governments around the globe want to protect business interests and enforce policies that restrict business activities. This often clashes with regulations that experts recommend for effectively addressing climate change. Without strong commitments from all participating countries and wide-scale international action, it becomes very difficult for any single state or group of states to adequately address climate change through legislation or otherwise.
Differences in power dynamics among countries further complicate gaining full consensus on how best to tackle climate change. Countries with more economic power may appoint themselves to be represented on international bodies for negotiations about the environment. This can lead the to divisive discussions between the countries' interests and the collective interest. At both the national and international level, there have been extensive discussions about potential side effects of radical changes like geoengineering.
At a grassroots level too, grassroots movements have struggled against powerful opponents including corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbies trying to maintain politically favorable positions for their industries especially when it comes to funding research into alternative forms of energy production or enforcing renewable energy technology mandates such as low emissions targets for vehicles etcetera - meaning individual governments must remain clearheaded about potential rewards and outcomes if they are going actively try to make valid progress on the matter in the question itself instead seeking public favor through short-term gains or even spectacles.
If we are to achieve a coordinated effort to address our current environmental crisis, it is crucial to properly distribute resources and be aware of political divisions among nations.
What does the role of greenhouse gases contribute to climate change?
Greenhouse gasses are key to climate change. They act like an invisible blanket surrounding the Earth, trapping the infrared radiation that warms it and keeping it from getting too hot. Without them, our planet would be much cooler than it is now.
These greenhouse gases are created by human activity such as burning fossil fuels. These activities are increasing in number, which means that more heat is trapped in our atmosphere. This can lead to extreme weather events and rising temperatures.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the largest greenhouse gas. This is due to fossil fuels like oil, coal, and gas. Other major contributors to climate changes include methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
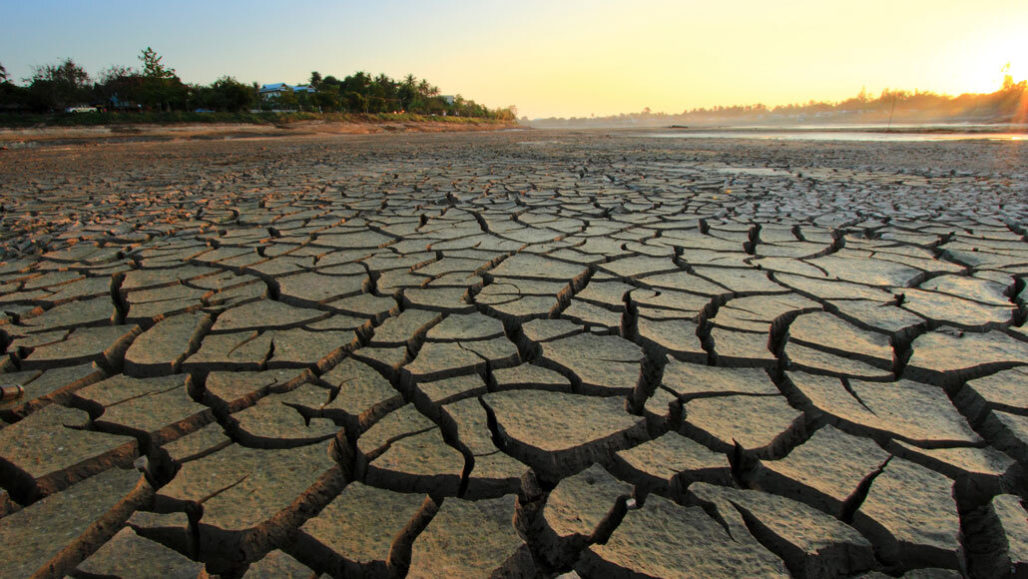
The concentration of greenhouse gases has increased significantly since preindustrial times due to human activities. Global warming has caused an increase in temperature all around the globe, and in our oceans. It is also leading to changes such as intense storms and droughts; melting glaciers; and rising seas.
Humans must reduce greenhouse gas emissions to avoid further climate change damage. This can be done by switching from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. There are also ways to reduce CO2 emissions, such as by planting trees and using agricultural techniques that absorb more of the gas. These activities will lower the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gasses and make the Earth a more healthy place for all life.
What are the impacts of climate change on society and the environment?
Climate Change has wide-ranging effects on the environment as well society. Climate change is causing a variety of environmental problems, including rising temperatures, extreme weather, sea level rise, and reduced air quality. These changes can have severe consequences for human populations. They can lead to instability, increased poverty, insect-borne diseases and altered migration patterns.
Already, climate change is having an enormous impact on the environment as well as societies around the globe. As global temperatures rise, it is likely that this trend will continue in the near future.
Global climate change has one of the most powerful effects on ocean levels. This causes shoreline erosion along many coastlines and increases the risk of flooding for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion can also happen, affecting freshwater supplies to coastal regions of many countries.
Extreme weather events such as heatwaves and droughts regularly occur across many countries around the world as a result of climate change. These events cause mass destruction to homes and businesses, leading to displacement or relocation of communities or wiping out whole towns in some cases. Extreme storms can also cause flooding and landslides, which increase the damage to infrastructure like roads and railways.
The increasing frequency of wildfires that are caused by climate change has also led to devastating consequences for both habitats and those living nearby.
Many people are forced to flee their homes due to drastic changes in their living conditions.
The increase in aridity causes dust storms to become more frequent, which makes people suffering from asthma and other respiratory ailments such as asthma even more vulnerable. Furthermore, pest infestations are predicted to rise in tandem with warmer temperatures. This phenomenon is known as the 'greenhousebug'. Global food insecurity will continue to grow as fewer crops have lower nutritional qualities. This could potentially lead to more hardships for people already struggling to make ends work.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Incorporate Sustainable Practices into Your Daily Life to Fight Climate Change
Reducing your consumption of energy and food is one way you can integrate sustainable practices into your day. Shopping secondhand and borrowing items from family and friends is a better option than buying new products every day. Eating vegetarian meals at least once a week can reduce methane emissions from livestock production. To conserve energy, it is a good idea to turn off all lights when you leave a room.
The other way to combat climate changes is to reduce carbon emissions from transportation such as cars and aircrafts. We can also opt for renewable power sources such as solar panels in replacement of traditional fossil fuels to generate electricity at home. For climate action to be effective, it is essential that we support policy measures that promote clean air regulations. In conclusion, it is extremely beneficial to work with others on issues like ending plastic pollution or deforestation. It creates more citizens who are aware and will act upon that knowledge.