
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 13 is a goal to reduce the impact of climate change. This target is focused on adapting and reducing greenhouse-gas emissions. SDG 13 targets are to improve resilience against climate-related hazards, increase knowledge about climate changes, and enhance early warning. The targets can be achieved to help achieve the goal of keeping global warming below 1.5 degrees Celsius.
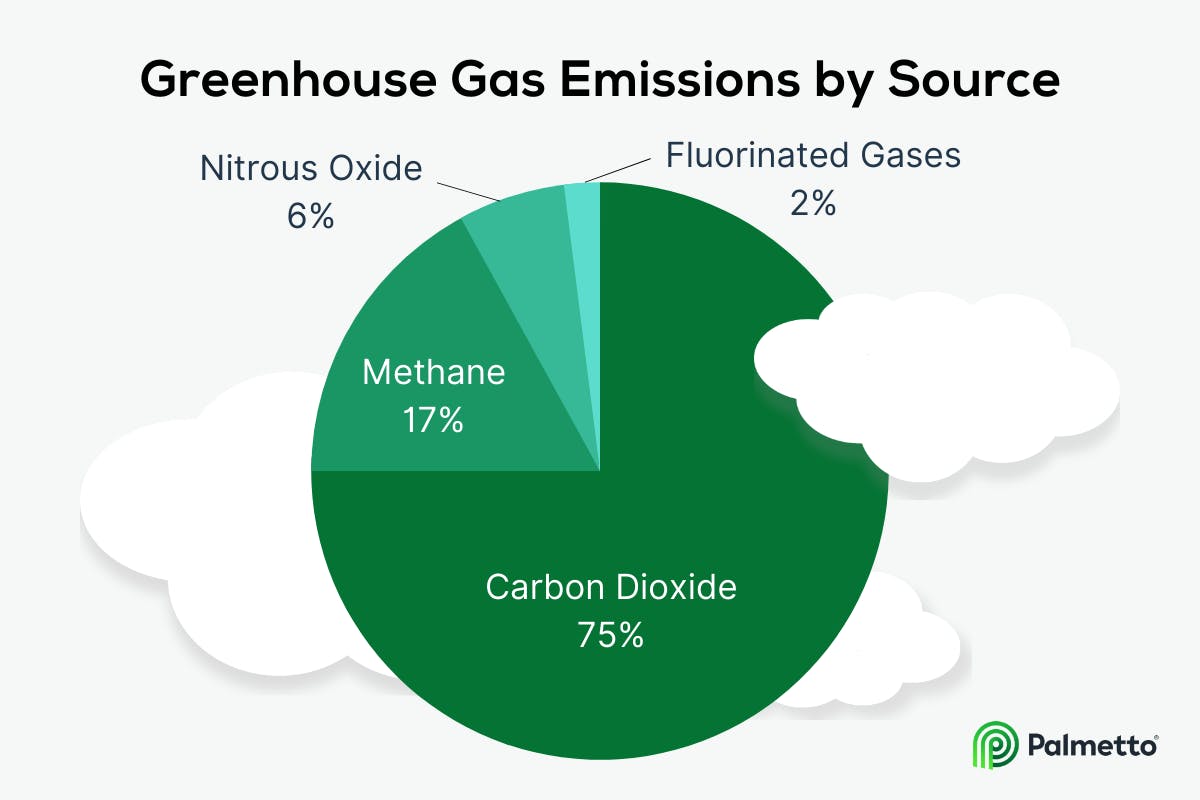
Climate change has a global impact on human systems, natural systems and social systems. This includes a rise in temperature, changes in precipitation patterns, and ocean acidification. These effects are caused by anthropogenic emission of greenhouse gases. To reverse climate change, countries need to address the problem from different angles. States must also improve the effectiveness their climate policies. These goals can be met by companies, which can reduce their carbon footprint and build resilience in their operations.
Despite growing awareness of the need for climate change mitigation, progress towards SDG 13 has not been consistent. Many of the indicators show progress, while others demonstrate that current commitments are insufficient to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement. These results are based on a disaggregated analysis of the Sustainable Development Goals. Countries should be focusing on energy efficiency at end-of-use, switching to renewable energy sources, and ensuring climate protection in national policies. These actions may bring short-term benefits, but they could take some time to pay off.
The SDG 13 monitoring report, released in March 2016, identifies indicators and shows how countries are moving towards these targets. The report also highlights possible links between the goals. It also outlines possible links between the goals. For example, countries can be more resilient to climate change by improving their forest management. An increase in investment in forest management can also help local communities adapt to climate change. Unsustainable forest exploitation can hinder synergies with the SDG as well as forest conservation.
Currently, only 3% of climate financing is dedicated to forest activities. The Paris Agreement sets 20% targets for improved forestry and landmanagement. These actions require long-term financing. It is crucial that countries work together with local communities and other countries to create these synergies. If these gaps are closed, there is a greater likelihood of meeting the goals of the Paris Agreement.
Despite the risks that climate change presents, more and more countries are taking action to adapt. Flood protection, improved agricultural practices and adaptable agricultural techniques are just some of the measures. Other adaptation measures include adaptation in economic activities and the building of knowledge and capabilities to adapt to climate change. Adaptation is essential to the achievement of the SDGs and other global development goals.
Climate change impacts all countries. The extent of the effects will depend on how large the country is, what the economy is doing, and where it is located. Some regions will be more affected by climate change than others. For instance, the saline intrusion of groundwater aquifers is having a negative effect on the water supply for agriculture. Sea levels rising will also have an impact on freshwater supplies.
FAQ
How does climate politics affect global efforts for its resolution?
Climate change is highly politicized and has caused division between governments, individuals, and nations. Politicians of many actors influence the implementation of actions to address climate change. It has been difficult to reach a consensus on the global effort to address this urgent environmental problem.
The overwhelming majority of scientists agree with the fact that human-generated global warming is real. It is urgent for action to address it. Politics surrounding these issues can often hinder global cooperation, which is required to make effective progress in implementing sustainability energy practices and upholding regulations protecting natural environments, researching viable technological options, and other climate-change interventions.
Most governments are eager to protect their business interests and enforce rules that will limit business activity as much as possible. This is often in conflict with the regulations experts recommend to combat climate change. Without strong international commitments and wide-spread international action, it can be very difficult for any individual state or group of nations to address climate change effectively through legislation.
It is difficult to reach a consensus about how to address climate change because of differences in power dynamics between countries. Countries with more economic power frequently appoint their own representatives for international negotiations over the environment. This can lead lopsided discussions between countries' perceived interests and those of all other parties. The potential side effects of radical change like geoengineering, have been extensively discussed at both the national level and internationally.
The grassroots movements also have struggled against powerful enemies, such as corporate ownerships and well funded lobbyists who want to maintain politically favorable positions in their industries. This includes funding research into alternative forms energy production and enforcing renewable technology mandates. It is important that individual governments are clear about the possible rewards and outcomes if they intend to actively pursue valid progress on this matter and not seek public favor through short-term gains and spectacles.
A coordinated effort to reduce our environmental crisis will only succeed if resources are distributed properly and there is no political divide between nations.
How can climate change impact food security and agriculture?
Climate change and global warming are directly impacting agriculture and food security. Changes in climate can have an impact on rainfall patterns, temperature, soil moisture, extreme weather, and other aspects of agriculture. This can impact farming activities, reduce crop yields, or cause loss of agricultural diversity. Warmer temperatures could lead to the growth of pests or diseases, which can have a negative impact on crops. This could lead to an increase in food prices and a higher incidence of hunger worldwide.
Rising sea levels present a new threat. They can inundate agricultural land in many coastal locations, leading to increased salinity in wetlands where important crops grow. Changes in climate also have an impact on livestock production. In summer, high temperatures can lower fertility rates in animals like sheep and cattle. This can result in lower milk yields, which can worsen food insecurity.
Global warming and climate changes are interrelated. But, governments around world are working to mitigate the effects of these changes through adaptation strategies. This means promoting sustainable methods, such as crop rotation and the preservation of native seed varieties. These strategies help prevent adverse effects from climate change or other environmental stressors. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Global farmers must adapt to climate change in order to ensure food security. Existing infrastructure must be improved to allow for the appropriate action when necessary. This includes stabilizing irrigation networks that have adequate access to water during periods when there are less water sources due either to extreme downpours or warmer climates. Collaboration between different stakeholders is needed to ensure that the quality nutrition guidelines are adhered to in all climates.
What is the role of individuals and communities in addressing climate change?
Climate change is a major contemporary challenge. It is an issue that affects everyone and requires our collective attention, as well as individual action, for us to make a difference.
Individuals play a key role in combating climate change and reducing its effects. A person's everyday behavior can range from cutting down on waste and conscious consumption to making lifestyle changes such as changing to vegetarianism or using public transportation less often and choosing eco-friendly clothing and home decor. They can also participate in political advocacy and help promote sustainable initiatives in their local communities.
They are also crucial in addressing climate issues on a wider scale. They can help reduce carbon emissions by promoting sustainable energy sources, improving infrastructure for electric vehicles and cycling, and encouraging waste management through composting. This mission requires collaboration between communities in different cities and countries.
Additionally, civic education about the dangers of climate change and ways to help it be tackled should be started in the very early stages of education. It should also be taught throughout lifelong learning opportunities. This will help people become more aware about the issues and to understand how they relate to others who are also affected by global climate change.
Employers have a significant responsibility in combating climate change. Introducing corporate practices that are focused on sustainability and choosing green alternatives whenever feasible will undoubtedly result in positive economic and sociological outcomes.
Thus, individual actions as well as community policies combined with business transformation will greatly contribute to the creation of solutions for global warming and collectively protecting humanity from longer-term harmful effects from climate change.
What impact does climate change have on biodiversity and ecosystems
Climate change has a range of impacts on biodiversity and ecosystems. The most pressing issues facing wildlife and ecosystems are rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and increased acidity.
These shifts in climate conditions can cause shifts in habitat areas, disrupt food chains or affect population numbers or species distributions, with potentially dramatic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning of ecosystems. The hydrological cycle changes can have an impact on the availability of water for aquatic species.
Climate change is also causing rising temperatures and more extremes like droughts/floods. This adds to the stress already placed on fragile systems such coral reefs and tropical rainforests. A climate change scenario could see up to 30% loss of animal species by 2050. That would trigger a chain reaction of losses within eco-systems.
Climate change is a serious threat to biodiversity as well as human societies that rely on functioning ecosystems for food and fresh water. It is essential to mitigate its effects at all levels. Future damages must be avoided by careful management.
What are the main causes of climate changes?
Climate change is a global phenomenon. It has been caused by an increase in greenhouse gases that are emitted from humans. These emissions lead to a greater amount of sun's energy being trapped in Earth’s atmosphere, which results in rising temperatures.
Other contributing factors to climate change are population growth, land clearance and destruction of ecosystems as well as deforestation, energy use, over-grazing and energy consumption. This reduces the amount of carbon sinks naturally found in the atmosphere that absorb CO2. Climate change can also be caused by natural forces like changes in solar radiation.
These combined human activities result in overloading Earth's capacity to properly balance its energy budget, leading to an average increase of 1 degree Celsius globally since pre-industrial times. As the oceans absorb most heat energy, glaciers melt more quickly than they form. Other damaging consequences include water scarcity and droughts or extreme weather events like floods and hurricanes caused by frequent heavy precipitation on saturated soils.
To prevent further damage, we must reduce our carbon footprint and cut our emissions as soon as possible. We can also take action now to mitigate the already severe effects of climate change. Along with reducing our dependence upon fossil fuels to generate electricity, it is important to invest in renewable sources like wind turbines or solar cells that do not emit harmful pollutants into nature. Reforestation and other sustainable practices can help restore balance to these delicate planetary cycles that we depend on for our survival.
Statistics
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest in Clean Energy, and Support the Transition to Low-Carbon Future
Clean energy is any form of renewable energy that doesn't produce or emit pollution. This includes technologies like solar photovoltaic and wind power, as well as hydroelectricity, geoelectricity, and hydrogen fuel cell. Investing in clean energy sources can have many environmental benefits, such as reducing reliance on fossil fuels, reducing the amount of air pollution generated by traditional electricity methods, and providing more reliable electrical access to remote locations.
By purchasing shares in companies that are developing new technologies in the sector, investors can become involved in clean energy projects. This could be done by investing in publically traded stock, mutual funds, or ETFs related to renewable energies. Direct investments in start-ups and venture capital projects can be an option for investors to help fund research and development of clean energy technologies.
Clean energy investors support innovation that reduces harmful emissions from electricity generation. This investment may lead to economic growth by creating jobs related the production of renewable energies that require skilled labor. The tax incentives programs that encourage investment into green technologies such as wind farms and solar panels can also provide investors with a financial reward.
We can both support the transition from low-carbon to a low carbon future by investing in companies that are focused on producing electricity from renewable resources like sun, wind, water and avoid activities that may harm the environment.