The United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 13(SDG 13), aims at reducing climate change impacts. This target is focused on adapting and reducing greenhouse-gas emissions. SDG 13 targets include improving resilience to climate-related hazards, increasing knowledge about climate change, as well as enhancing early warning. To achieve the goal, the targets must be met.

The impacts of climate change affect human systems, natural systems, and social systems globally. This includes a rise in temperature, changes in precipitation patterns, and ocean acidification. They are caused by human-caused greenhouse gas emissions. To reverse climate change, countries need to address the problem from different angles. The effectiveness of climate policies must be improved by governments, among other things. Companies can play a role in achieving these goals by reducing their carbon emissions, increasing their resilience, and scaling their low-carbon products.
Despite growing recognition of climate change's importance, SDG 13 progress has been slow. Many indicators indicate progress while others reveal that the current commitments have not been sufficient to reach the Paris Agreement's goals. These results are based upon a disaggregated assessment of the Sustainable Development Goals. It is important that countries focus on improving energy efficiency at the end of their lives, switching to renewable energies and making sure that climate-friendly policies are implemented in their national policies. These actions may bring short-term benefits, but they could take some time to pay off.
The SDG 13 monitoring Report was published in March 2016. It identifies indicators, and shows how countries are working towards these targets. It also lists possible links between the SDG 13 goals. The ability to increase the resilience of forests to climate change could help countries achieve their goals. A greater investment in the management and protection of forests can help improve the ability of communities to adapt to the effects of climate changes. Unsustainable forest exploitation may hinder synergies among the SDG, forest conservation and other initiatives.
Forest actions receive only 3 percent of climate finance. Better forestry and land management can contribute up to 20% of the targets set by the Paris Agreement. These actions require long-term financing. It is crucial that countries work together with local communities and other countries to create these synergies. If these gaps are closed, there is a greater likelihood of meeting the goals of the Paris Agreement.

Despite the potential dangers of climate change, more countries are taking measures to adapt. These measures include flood protection and improved agricultural practices. Other adaptation measures include adapted economic activities and building knowledge and capacity to respond to climate change. The achievement of the SDGs is dependent on adaptation.
All countries are affected. However, the severity of the effects will depend upon the size of the region, the economy and the population. Some regions will suffer more from the effects of climate changes than others. The saline infiltration of groundwater wells is affecting the supply of water for agriculture. Sea levels rising will also have an impact on freshwater supplies.
FAQ
What is the current state of international efforts to address climate change?
International efforts to combat climate change are moving at a remarkable pace and with unprecedented unity. Countries around the world are increasingly collaborating on ways to reduce emissions, strengthen resilience against impacts, and invest in renewable energy sources.
The Paris Agreement is an international framework that encourages collective action. It also provides a framework to allow individual countries and regions to set voluntary targets to reduce emissions. Additionally, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is providing political guidance and piloting new initiatives such as carbon market mechanisms.
There are also progresses in certain regions. For example, the European Green Deal, a comprehensive package aimed at recreating Europe’s economy with sustainability at the core, and the African Renewable Energy Initiative, which targets increasing Africa's share in global renewable energy production, is being implemented.
In addition to policy developments, action can be seen across sectors and industries; cities are actively transitioning toward sustainable public transport systems while society as a whole is embracing more sustainable lifestyles; companies are innovating technologies that drive down emissions while investors are reallocating their capital away from fossil fuels towards renewables.
Through the Common Reporting Framework (CFR), the 2021 Guidelines, the rich countries that are members of the OECD committee have agreed to common standards for reporting their national climate change actions.
All of these efforts show an unprecedented focus on climate action. If there is any hope of meeting the science-based Climate Goals, all stakeholders (governments, civil societies, and private sectors) must continue to build on their momentum and push for greater ambition & progress.
What impact does politics have on global efforts to tackle climate change?
Climate change is a controversial issue that has caused a lot of division between nations, governments and individuals. Politics of different actors can have an impact on the implementation of climate change measures. It has been difficult to reach a consensus on the global effort to address this urgent environmental problem.
The overwhelming majority of scientists agree with the fact that human-generated global warming is real. It is urgent for action to address it. These issues are often subject to political interference that can hamper global cooperation in order to implement sustainable energy practices, preserve natural habitats, find viable technological solutions and other interventions related to climate change.
Many governments in the world want to protect their economic interests, and enforce measures that limit business activities. This often conflicts with the regulations that experts recommend to address climate change efficiently. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
Differences in power dynamics among countries further complicate gaining full consensus on how best to tackle climate change. The countries with greater economic power tend to nominate their own representatives to represent them in international bodies that are responsible for the environment. This can lead to biased discussions between the perceived interests of the country and the collective interest of all parties. The potential side effects of radical change like geoengineering, have been extensively discussed at both the national level and internationally.
Also at the grassroots level, grassroots movements have fought against powerful opponents such as corporate ownerships. These lobbies are trying to preserve politically favorable positions for their industry especially when it is about funding research into alternative sources of energy production or enforcing Renewable Energy Technology mandates. If individual governments want to make valid progress in the subject matter themselves instead of seeking short-term benefits or spectacles, they must be clearheaded about possible outcomes.
To mitigate the current environmental crisis, it will be crucial that resources are properly distributed and political divisions between countries are not overlooked.
What does the role of greenhouse gases contribute to climate change?
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act like an invisible blanket around the Earth, trapping infrared radiation and warming the atmosphere. Without them, the planet might be much colder that it is now.
Greenhouse gases are generated through human activity, such as burning fossil fuels or other industries that produce emissions. These activities are increasing in number, which means that more heat is trapped in our atmosphere. This can lead to extreme weather events and rising temperatures.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the largest greenhouse gas. This is due to fossil fuels like oil, coal, and gas. Major contributors to climate disruption are methane (CH4) as well as nitrous dioxide (N2O) and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Due to human activities, the concentration of greenhouse gasses has increased dramatically since preindustrial time. Global warming has resulted in an increase of temperatures around the world and in our oceans. It is also causing drastic changes, such as increased storms, droughts, melting glaciers and rising ocean levels.
To prevent further climate change-related damage, humanity must reduce its greenhouse gas emissions by moving away from fossil fuels and towards renewable energy sources like wind or solar power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These actions will reduce the atmospheric concentrations and improve the environment for all living things on Earth.
What are the most effective solutions for climate change?
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our times, requiring urgent attention from governments, businesses, and citizens alike. The signs of a disturbed climate system include rising temperatures, extreme weather and sea level rises, as well as melting polarice. Many solutions have been offered to this problem, ranging from technological and behavioral solutions to geoengineering.
Technological solutions: A wide range of technologies have been used to address climate change. These include renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power. They provide reliable and clean energy with minimal impact on the environment. By replacing petrol cars, electric cars that are powered by renewable energy can significantly reduce the amount of air pollution in cities. Other technological solutions include projects to increase carbon sequestration within trees and soil, as well coastal protection systems that protect vulnerable places from rising oceans.
Making behavioral changes: Simple changes to routines can make a huge difference in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and limiting future climate disruption. For example, local production of goods and shorter supply chains can help reduce the emissions associated with transport costs. Also, using public or active transport instead of personal cars optimizes the use and reduces cost and air pollution. Additionally, home insulation that is more efficient can reduce dependence on gas boilers for heating your homes and lowers emissions.
Geo-engineering : Geo-engineering refers to large-scale interventions in natural system that have been deemed too risky for potential unforeseen results.
The effectiveness of these solutions largely depends on how much producers commit themselves towards investing in green alternatives; currently, initiatives such as using electric Cars tend expensive when compared with petrol versions however economic incentives favoring green investments play an integral role in incentivizing alternative solution uptake otherwise these remain mostly dormant when exposed only market forces which cannot guarantee their utility over time try apart from increasing consumer awareness over time regarding their efficiency hence mandating alternative solutions via policy measures represents one way forward however this needs regulatory bodies willing committed enough engaging players involved further still nontechnological approaches work one level but solving global warming phenomena requires all parties involved tackling issue earnest together.
How does human activity contribute to climate change?
Climate change can be attributed to human activity. In fact, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), humans are responsible for more than 70% of all global warming since the mid-20th century.
The release of carbon dioxide from fossil fuels: When fossil fuels are used, like coal, oil, or gas, they cause the atmospheric formation of carbon dioxide. This adds to already existing levels of atmospheric CO2, which act as a "greenhouse gas" by trapping heat from the sun in Earth's atmosphere and increasing temperatures even further. As Arctic ice melts, this causes ocean levels to rise and can cause severe weather patterns all over the globe, including floods, droughts and storms that could lead to food shortages.
Deforestation is the removal of trees that store atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks. This happens when they use it during photosynthesis. Deforestation also raises albedo (the amount of reflected solar radiation that is returned into space) and reduces solar heat absorption by earth's surface, thereby promoting global warming. Deforestation is also associated with respiratory problems and local air quality.
Farming: The animal agriculture industry contributes 14%-18% of total anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases globally every year. Large amounts of methane gas are released by animal waste due to its richness in methane bacteria. Eating less or none of these products can reduce global warming.
In conclusion, human activity has been drastically impacting our environment for centuries now, but with rapid advances made in technology such as renewable energy sources availability we have started turning our heads towards the future leaving behind carbon-emitting heavy industries results will soon start speaking themselves clearly when we leverage on technology through green innovation paving away toward eco-friendly efforts combatting climate change efficiently keeping everyone safe under prosperous nature purview.
What happens to developing countries when they experience the climate change effects?
Developing countries and communities are particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change due to limited access to resources, healthcare systems, and technology. Climate change can increase the pressure on already limited resources. Floods and droughts can also cause damage to already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can cause decreased crop yields. This will have a significant impact on poorer communities suffering from food insecurity. Extreme weather events like heatwaves or hurricanes can lead to destruction of infrastructure, displacement of people and further perpetuating economic inequality.
Climate change has long-term consequences. They will lead to continued resource scarcity, extreme poverty, and adverse health effects, including increased incidences of vector-borne illnesses like dengue fever and malaria. In addition, there will be a higher risk of flooding due to rising sea levels coupled with extreme weather events putting lives at risk in coastal areas where populations often lack the adequate infrastructure or emergency services needed for evacuation. To build resilience against these risks, mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions is necessary. Other measures include improved management and better access to water resources.
How does climate change affect extreme weather events?
Global warming has directly affected extreme weather phenomena such as heatwaves. Global warming has caused an increase in atmospheric temperatures. This has had an impact on different weather phenomena worldwide.
According to climate scientists, the frequency of extreme weather-related catastrophes has more than doubled in the past 20 years. Sea levels rise as a result of changing wind patterns and ocean temperatures. This alters the normal distributions of storms, hurricanes, and other weather phenomena in different geographical areas around the globe.
The 2015 El Nino event brought warm water toward South America. It caused alarmingly high temperatures and heavy rains, which led to flooding in Peru. These floods resulted in displacement of people and property destruction. Many locations, including Antarctica recorded their highest ever temperatures. This shows that there is a clear relationship between global warming trends with the occurrence or frequency extreme weather events.
Another example is Hurricane Irma in 2017. It caused $50 billion economic loss to Florida and other states, as well as Puerto Rico and Cuba. This is yet another proof that climate change is responsible.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), concluded human activities are increasing climate change's severity. This in turn leads to more frequent and severe natural disasters across the globe. Therefore, strong evidence is available regarding our relationship with extreme weather events happening at frequent intervals all around us.
Statistics
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
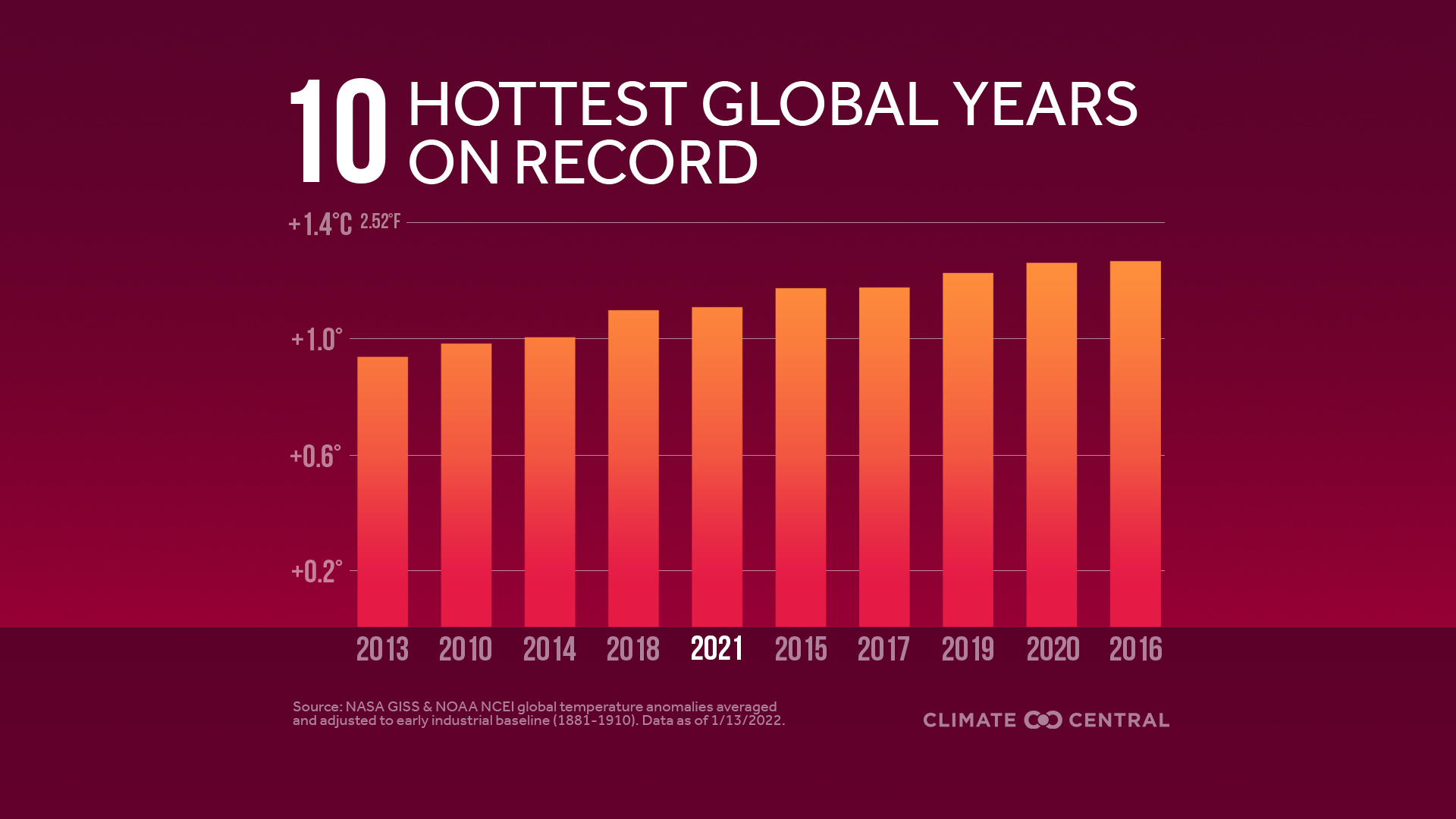
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
External Links
How To
How to Educate your Community about Climate Change and Mobilize Action
Many forms of climate education are available, including interactive educational tools and online resources, as well as classroom activities, simulations, or experiential learning programs. These are the key components of climate change education.
-
arming people with practical knowledge about the subject
-
Demonstrating how individuals can make a difference
-
Involving participants in an open dialog about potential solutions
-
inspiring action through shared experiences
By providing comprehensive climate change lessons for both students and adults alike, educators will be able to help their communities develop strategies for reducing their environmental footprint.
Connecting scientific research and real-world examples creates a unique opportunity to engage audiences in a meaningful discussion. The best practices and case studies can provide participants with the chance to experience positive outcomes firsthand. This can help them innovate or create replicable measures in their own communities.
Incorporating action-oriented activities into educational curriculums empowers participants with the mental tools they need -- such as creating campaigns, forming petitions, or local actions -- enabling them to become agents of social and political transformation or sustainability improvement initiatives. A focus on individual agency emphasizes the importance and benefits of participation in reducing carbon emissions. However, it also highlights participants' collective contribution to a larger end result. A key element in policy-making is to involve stakeholders as early as possible. This encourages their active involvement at every stage of the process and could result in better outcomes for all. Through concerted efforts at increasing public understanding of the impacts of climate change coupled with taking appropriate action on mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, we might be able to create an environment where these pressing matters are addressed urgently with attention applied where necessary most so that together we may one day be able to ensure successful implementation measures that will help us reach our collective goals out ahead time as well.