A cryosphere is a portion of Earth's surface that includes ice sheets, ice caps, sea ice, lake ice, river ice, and frozen ground. It is an integral part of the climate system. Cryosphere impacts include changes in temperature, precipitation, and circulation. This area provides water resources for ecosystems. Regulating ocean currents can also be regulated by glaciers and ice sheet. In addition to these effects, it is a major source of methane.
Many parts of the cryosphere are understudied. There are many types ice and snow that cover the Earth from the Arctic to Antarctica. The snow can act as an insulator and delay the annual cycle of energy. But, this effect does not occur in every area. Some areas of the Arctic have a higher albedo than others. These areas absorb more sunlight. These areas will warm up as the planet warms.
Sea level will rise because of the melting of ice, snow, and other ice. This is a serious problem. It will have a devastating effect on all the coastal communities. Additionally, it will lead to more acidic seas. Mid-latitude weather can also be affected if there is a decrease in ice mass. Changing oceans will affect the marine ecosystems that feed the world's population. Also, warmer temperatures may allow for longer Arctic growing seasons.
The rate of warming will be affected by sea ice loss and permafrost melting. Research has shown that if we continue to burn fossil energy at the current rate, we can expect to see a quarter of permafrost to melt by 20100. This represents more than a double of the Arctic contribution towards global warming. At this rate, the loss of ice will make an even bigger impact on the planet. Even if we stop burning fossil fuels tomorrow, warming impacts would still occur, especially in coastal regions.
Permafrost has high carbon content. If it thaws, it releases a huge amount of methane, which is a greenhouse gas. A thaw can also lead to the death of frozen animals and plants. Once these processes are in place, methane could accelerate the rate for warming. Permafrost can release between 300 and 600 million tonnes of net carbon every year if it is thawed.

Detailed records of past climate can be found in layers of ice and glaciers. In addition, it is estimated that permafrost is the second-largest source of carbon on the planet, after the atmosphere. Currently, permafrost is covered with about one-and-a-half billion tons of carbon. By the end, it will be more than three hundred million tons.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) recently released a special report on the impact of climate change on oceans and land. Although the cryosphere isn't well understood, it can be a useful indicator of future climate change. They concluded that the world's oceans are crucial to the health and well-being of the planet. The impact of these changes on the planet will affect everyone.
FAQ
How does the politics of climate change impact global efforts to address it?
Climate change has become a highly politicized topic that has caused great divisions among governments, nations, and individuals. Politics of different actors can have an impact on the implementation of climate change measures. It has been difficult to reach a consensus on the global effort to address this urgent environmental problem.
The vast majority of scientific opinion agrees that human-generated climate change is real and requires urgent action. These politics often hamper global cooperation needed to achieve effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices.
Many governments around the globe want to protect business interests and enforce policies that restrict business activities. This often clashes with regulations that experts recommend for effectively addressing climate change. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
Further complicating the process of reaching full agreement on how to deal with climate change is the differences in power dynamics. The countries with greater economic power tend to nominate their own representatives to represent them in international bodies that are responsible for the environment. This can lead to biased discussions between the perceived interests of the country and the collective interest of all parties. In addition, potential side effects from implementing radical changes such as geoengineering have been debated heavily at both national and international levels.
The grassroots movements also have struggled against powerful enemies, such as corporate ownerships and well funded lobbyists who want to maintain politically favorable positions in their industries. This includes funding research into alternative forms energy production and enforcing renewable technology mandates. It is important that individual governments are clear about the possible rewards and outcomes if they intend to actively pursue valid progress on this matter and not seek public favor through short-term gains and spectacles.
It is essential to distribute resources properly to any intervention program, and to be mindful of political divisions within nations, if we want to see an effective coordinated effort to mitigate our current environmental crisis.
What are the consequences of climate change for society and the environment?
Climate Change can have broad impacts on society as well as the environment. Climate change has many environmental effects. These include rising global temperatures, increased extreme weather events and sea level rise. These changes can have serious implications for human populations, creating instability in communities, intensifying poverty and insect-borne diseases, altering human migration patterns, and destroying vital habitats.
Already, climate change has had a broad range of devastating effects on society and the environment around the globe. As global temperatures rise, this trend is likely to intensify in the near term.
Ocean levels rising due to melting ice caps is one of the most pervasive effects of climate change worldwide. This causes shoreline erosion along many coastlines and increases the risk of flooding for coastal communities. Also, saltwater intrusion occurs, which negatively affects freshwater supplies in coastal areas in many countries.
Due to climate change, extreme weather phenomena such as heatwaves/droughts frequently occur across many countries in the world. These extreme weather events can cause widespread destruction of homes and businesses. In some cases, they lead to the displacement or relocation or even complete destruction of entire towns. Additionally, severe storms pose additional risks due to flooding or landlides that can increase damage to infrastructure such roads and railways.
Additionally, wildfires caused climate change are more common than ever. They can be devastating for both the habitats and the people who live nearby.
Many people are forced to flee their homes due to drastic changes in their living conditions.
An increase in aridity means that dust storms can occur more frequently, making people with asthma and other respiratory illnesses like asthma particularly vulnerable. Furthermore, pest infestations are predicted to rise in tandem with warmer temperatures. This phenomenon is known as the 'greenhousebug'. Global food insecurity will continue to grow as fewer crops have lower nutritional qualities. This could potentially lead to more hardships for people already struggling to make ends work.
What are some possible solutions to climate change, and how effective are these solutions?
Climate change is an urgent issue, and it requires immediate attention from government, business, and citizens. An unstable climate system can be seen in rising temperatures, extreme events, high sea levels, and melting of polar ice. Multiple solutions have been proposed to address this phenomenon. These solutions range from technological solutions to behavioral changes to geoengineering.
Technological Solutions: An array of solutions have arisen to address climate change through changes in technology. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power provide reliable, clean energy that has minimal environmental side effects. Electric cars powered entirely by renewable energy could replace petrol vehicles and significantly reduce pollution. Other technological solutions include reforestation projects that aim to increase carbon sequestration in trees and soil as well as coastal protection systems to protect vulnerable places against rising ocean levels.
Behavioral changes: Small adjustments to existing routines can make big differences in reducing emissions. This will help limit future climate disruption. So, for example, buying locally-produced goods reduces the transport costs associated with food transport. Also, using public or active transport instead of personal cars optimizes the use and reduces cost and air pollution. Additionally, home insulation that is more efficient can reduce dependence on gas boilers for heating your homes and lowers emissions.
Geo-engineering : Geo-engineering refers to large-scale interventions in natural system that have been deemed too risky for potential unforeseen results.
The effectiveness of these solutions depends on how committed producers are to investing in green alternatives. At the moment, electric Cars can be more expensive than petrol-powered versions. However, market forces that cannot guarantee their utility over the long term try to increase consumer awareness about their efficiency. This is why mandated alternative solutions via policy measures is one way forward. However regulatory bodies need to be willing to engage further players. While nontechnological solutions may work at one level, solving global warming must be tackled by all parties.
What is the impact of climate change on biodiversity and ecosystems?
Climate change has many effects on biodiversity and ecosystems. Rising temperatures, changes in extreme weather events and sea levels, as well as increased acidity in the ocean are just some of the issues affecting wildlife and ecosystems today.
Changes to climate conditions can have drastic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning ecosystems. Water availability can be affected by changes in hydrological cycles.
Climate change can also lead to rising temperatures and more extremes, such as droughts or floods. This places more strain on already fragile systems like coral reefs, tropical rainforests, and other ecosystems. A climate change scenario could see up to 30% loss of animal species by 2050. That would trigger a chain reaction of losses within eco-systems.
Climate change is therefore a considerable threat not only to biodiversity but also to human societies that depend on functioning ecosystems for food, fresh water, timber, and other services. It is essential to mitigate its effects at all levels. Future damages must be avoided by careful management.
What can we do to limit or mitigate the impacts of climate change?
There are various measures that can be taken to reduce and mitigate the effects of climate change. These include reducing greenhouse gases emissions by using better energy practices and other sources of electricity, improving land management, protecting forests and wild places, protecting against extreme weather, investing in sustainable transport, strengthening early warning system for disasters, starting a research programme on the impact climate change has on biodiversity and ecosystems. Also investing in green technologies like solar cells or wind turbines, encouraging sustainable consume habits, and implementing environmental regulations across all segments of society. It is important to raise awareness of climate change in order to encourage people and make them feel responsible for their actions.
How can we address climate change by addressing the role of the energy industry?
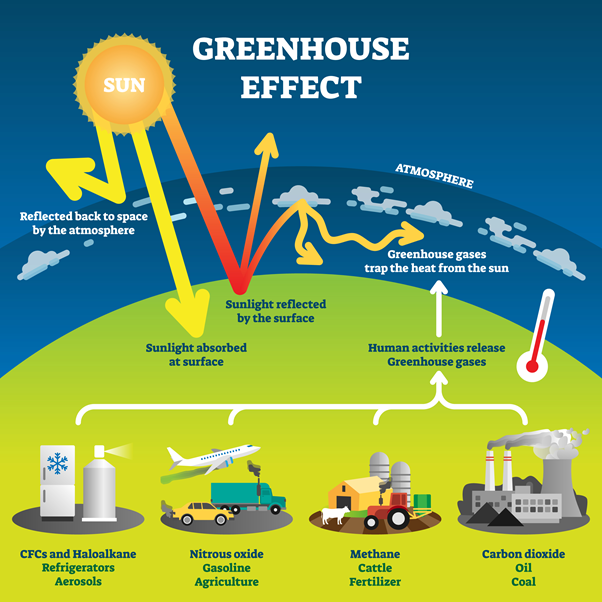
The importance of the energy industry in climate change mitigation is enormous. The main source of global warming comes from the burning of fossil energy. It releases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, traps heat, and results in an increase on Earth's average temperature.
This requires energy sources to move away from carbon emitting sources like natural gas and coal, and instead shift towards renewable energy sources, such solar, wind, or geothermal. This can be achieved through incentives and government policies, but also by investing in new technology like hydrogen fuel cells. By investing in infrastructure that supports the use of these renewable sources, businesses and households can drive down emissions while simultaneously reducing their electricity bills.
Another option is to move away from polluting transport options such as petroleum-fueled vehicles and towards electric cars or public transport. It is possible for governments to support battery technologies research and encourage people to use cleaner transportation.
Companies must also adopt green business practices to reduce their carbon footprint. This includes installing better insulation in offices and implementing energy efficiency plans at production plants. This can drastically reduce operational expenses while also improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives must be championed not just at the company level but also at the government level for them to be truly effective; increasing taxes on pollution products encourages individuals to switch away from harmful practices without forcing them financially outcompeting polluters by providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products will create an ongoing market to support sustainability efforts moving forward. In conclusion, tackling climate change requires a massive effort from both private industry and private citizens alike; switching to clean energy sources and adopting green practices are key aspects of fighting global warming which will positively affect generations now and are yet to come.
What is the impact of land use change and deforestation on climate change?
Deforestation and land use change have a direct and immediate impact on the climate. If trees are cut down, or burned, carbon dioxide, one the most important greenhouse gases, is no longer absorbed. Deforestation and burning of trees for agricultural purposes removes less carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
At the same time, changes in land use can also release more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. When forests are cleared for livestock production, the use of fertilizer and pesticides may lead to an increase in methane or nitrous oxide emissions. Additionally, clearing soils rich in carbon can increase the exposure; soils that are disturbed by farming activities or turned over can release more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
Deforestation and land-use changes can have a significant impact on regional air quality. As an example, deforestation smoke has been shown to reduce visibility and cause respiratory illnesses such asthma and other conditions. Because of the reduced amount of aerosol particles in our atmosphere, which scatter sunlight off the Earth's surface, these changes can have a cumulative impact on global climate.
In conclusion, deforestation and land-use change have resulted in a significant contribution to increased levels of global greenhouse gas emissions and have had negative impacts on local air quality that further contribute to climate change. Reducing these practices should be a high priority if serious efforts toward mitigating climate change are to take place promptly.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Reduce Your Carbon Footprint & Fight Climate Change
There are many ways you can reduce your carbon footprint and combat climate change. You can reduce the amount of energy you use in your home by installing energy-efficient lighting and insulation. It is possible to save energy by not using electronics, taking public transit, walking or driving and setting the thermostat lower in the winter and the summer.
Second, try to recycle and compost all food scraps. It will help prevent them from ending up in landfills that emit methane gas. Third, plant trees around your home for shade and natural cooling since vegetation absorbs carbon dioxide from the air. Finally, consider purchasing products with minimal packaging or sustainable labelings such as organic cotton or FSC-certified wood which means it's been sustainably managed over time to ensure forest health.
You can help reduce your personal emissions by supporting organizations such as Emissions Reduction Alberta, Climate Change Solutions; The Pembina Institute and The Nature Conservancy Canada. These organizations work to lower emissions through clean energy investments. They also support international initiatives such ICLEI – Local Governments for Sustainability's Urban Sustainability Strategies program.
We can all make small changes in our daily lives to combat climate change!